FAQs of Large Language Models
The notes aims to provide a systematic and concise introduction in Q&A form to the fundamentals of Large Language Models, serving as a knowledge base for beginners or interviewees. It is motivated by the fact that existing general ML FAQs repos(1, 2, 3) are not up-to-date in Natural Language Processing tasks, due to fast advancements in LLMs.
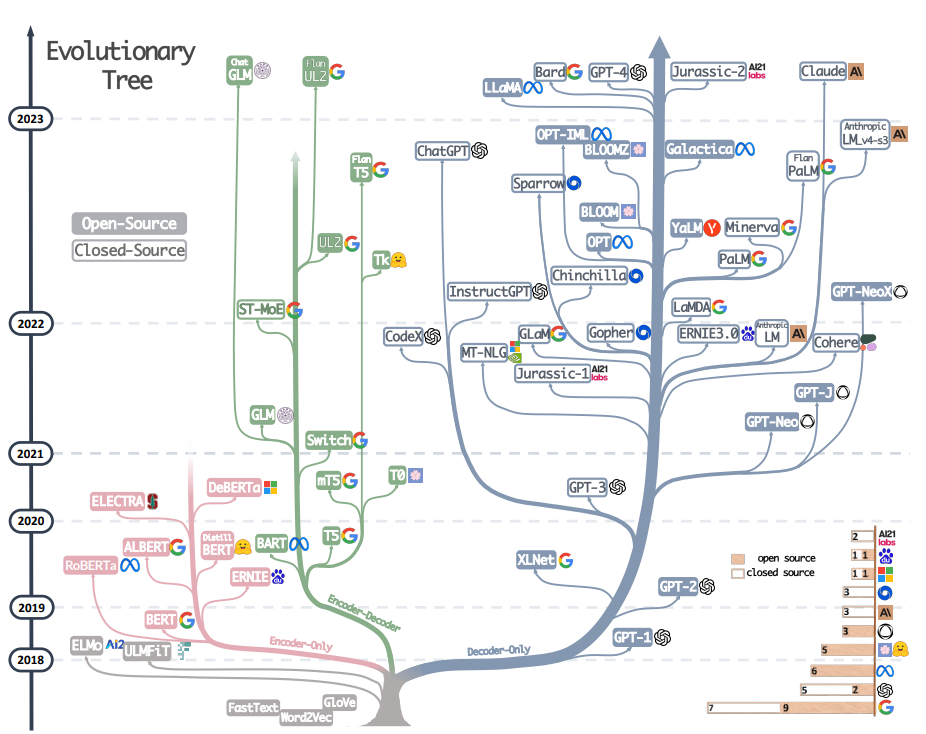
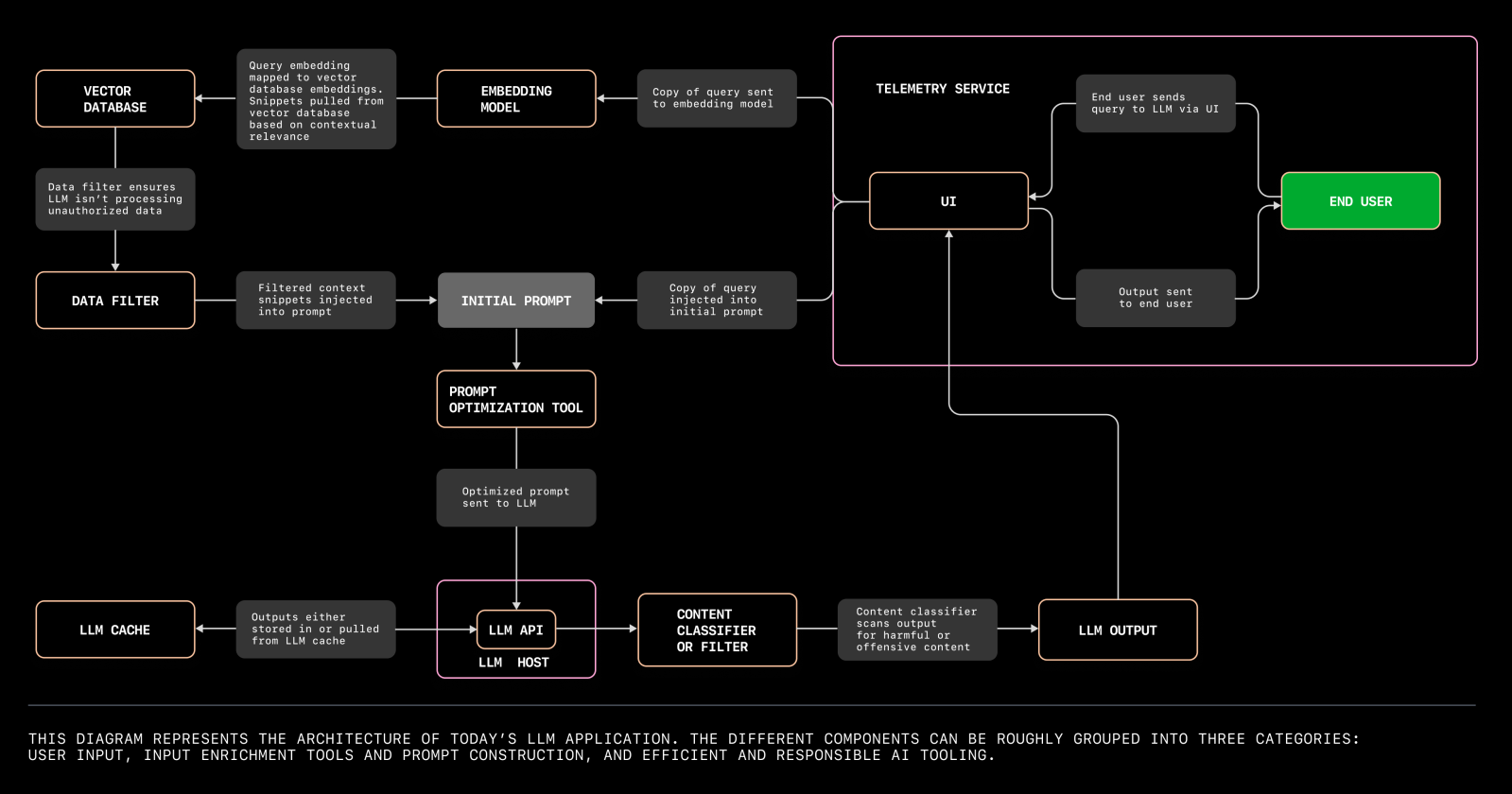
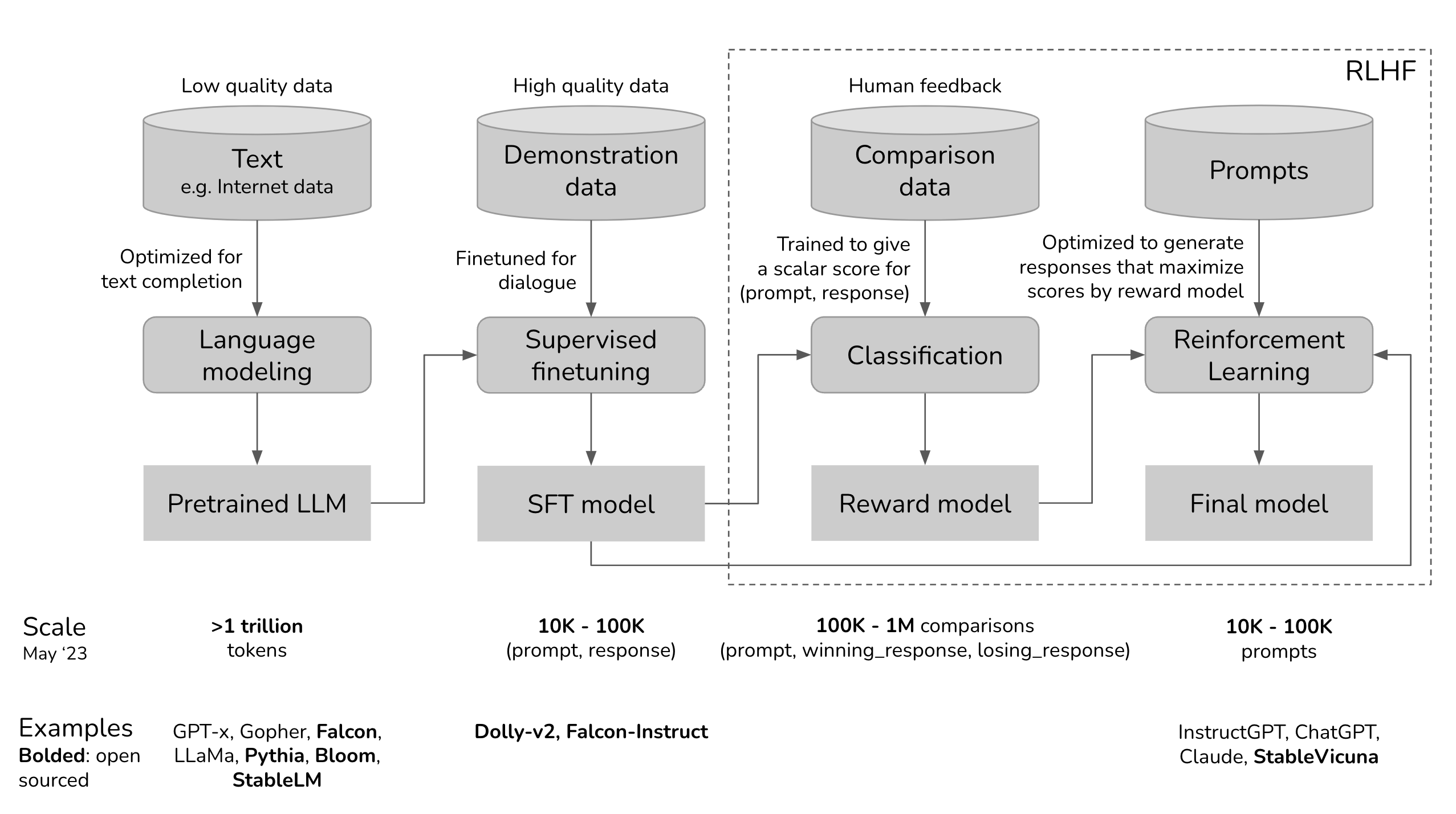
After reading this blog, you should be able to understand the following diagrams.
 |
|---|
| Applications of LLM as a service. Credit: Nicole Choi |
 |
|---|
| Diagram of training Large Language model. Credit: Chip Huyen |
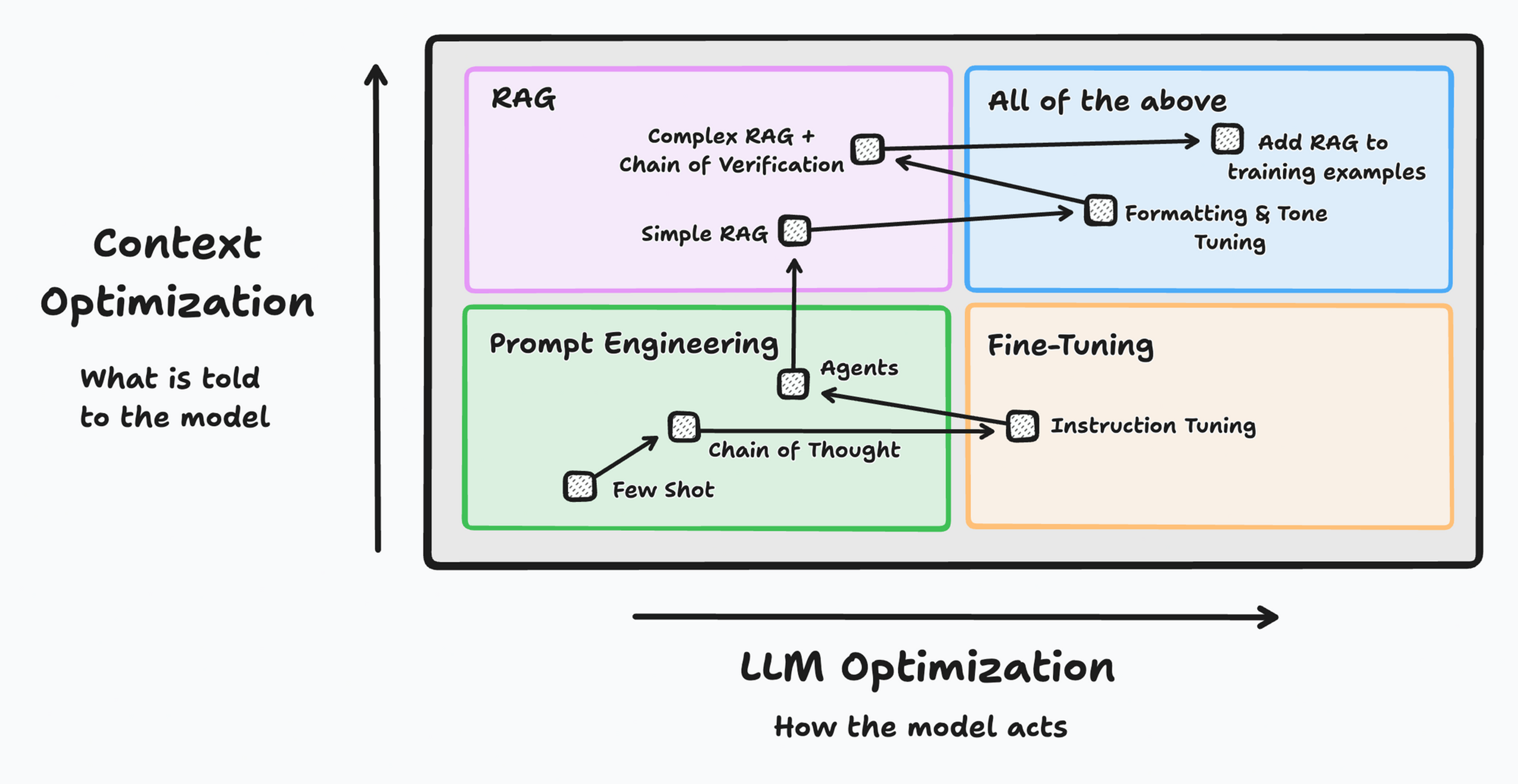 |
|---|
| Improving LLM Performance . Credit: Miguel Carreira Neves |
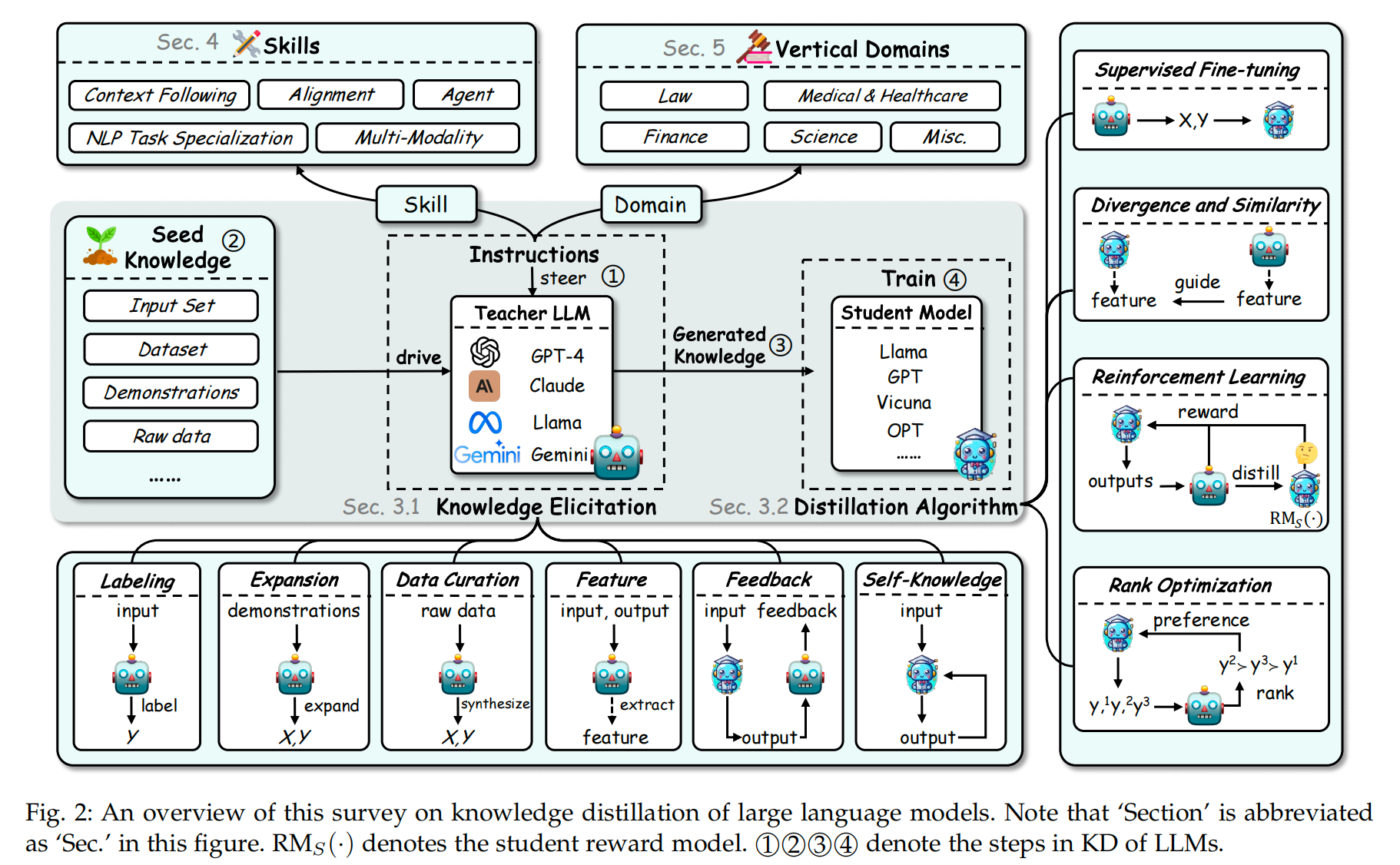 |
|---|
| Diagram of knowledge distillation. Credit: Xu et. al 2024 |
1. what is word embedding?
“embedding” originates from mathematics, referring to how one instance of a structure/space/set is contained within another instance. As a method of natural language processing, word embedding maps the space of natural language into a normed vector space, such as Euclidean space. It is a numerical representation of words and phrases that aims to capture not only the meaning of words and phrases, but also reflect the semantic relationships by their norm-induced distance.
Such requirement of word embedding, referred to as linguistic regularities (Mikolov et al, 2013) depends on a manifold hypothesis on the space of natural language, assuming that high dimensional numerical representations of words or phrases tend to lie near a low dimensional manifold.